There are four startup scenarios requiring that requires synchronization between the Host and Module:
...
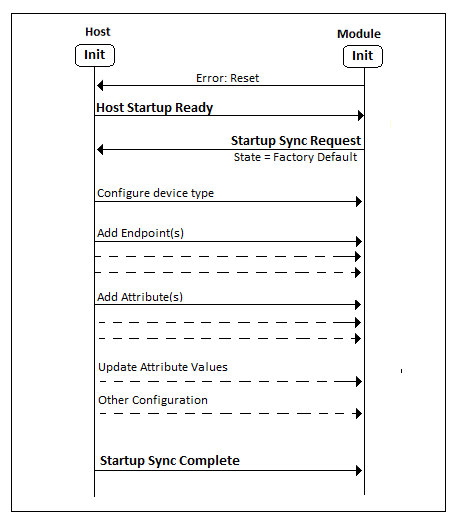
Upon startup, the Host must issue the the Host Startup Ready command command. On receiving the the Startup Sync Request command command will be sent from the Module , to the Host(see figure 1 for an alternate sequence). The Host may then enter the Startup Synchronization sequence to perform the aforementioned configuration of the endpoints, clusters and attributes. The Startup Sync Request command from the Module will include information on which application configurations may be restored from external flash and which the Host must reconfigure.
The Host completes the phase by sending the the Startup Sync Complete command command to the Module.
This page provides illustrated examples of the Startup Synchronization sequence.
...
Startup Synchronization Sequence
The primary commands sent and received in the Startup Sync Sequence are:
- /wiki/spaces/SPRHA15/pages/37093429 (Host → Module)
- /wiki/spaces/SPRHA15/pages/37093429 (Module → Host)
- /wiki/spaces/SPRHA15/pages/37093429 (Host → Module)
The diagrams in this section illustrate the Startup Synchronization sequence.The following figure
First Time Startup Configuration Sequence
Figure (1) illustrates the expected Startup Synchronization sequence following the first power up of the Module from its factory default state. In this diagram, the Configuration and Updates phase from the previous figure has been expanded to show key operations performed by the Host.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Startup Synchronization Request Retries
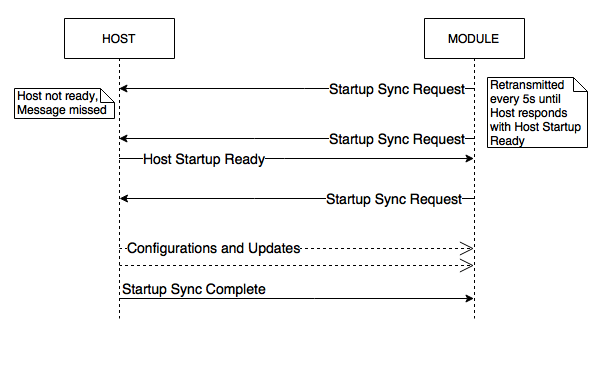
Figure (2) illustrates the sequence when the Module initializes more quickly than before the Host (described in scenario (2)). The Module retries the In this scenario the Module starts sending Startup Sync Request periodically(every 5 seconds) to ensure that the Host receives the message even if the Host starts up slower than the Module. You can see in the figure, the Host Startup Ready command is sent after the Startup Sync Request. The Module is required to send a final Startup Sync Request after receiving the Host Startup Ready command. The Host can now start the Configuration sequence.
Upon the Host completing synchronization (by performing all necessary configurations and updates) it will transmit the Startup Sync Complete command to the Module, at which point the Module will initiate the full application, i.e., commence network activities, etc.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Figure 2: Startup Synchronization Request Retries
Note: please note there is an error in the above diagram. The final Startup Sync Complete message should be going from the Host to the Module and not in the direction shown.
The next figure illustrates the expected Startup Synchronization sequence following the first power up of the Module from its factory default state. In this diagram, the Configuration and Updates phase from the previous figure has been expanded to show key operations performed by the Host.
...
The next figure
Subsequent Startup Configuration Sequence
Figure (3) illustrates the Startup Synchronization sequence after power up of a configured Module (i.e., subsequent to the state achieved in the previous previous figure 2). The application device type does not need to be defined as it is preserved in non-volatile memory. All configured endpoints, clusters and attributes are stored in volatile memory and must be re-configured after any soft or hard reset of the Module.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
Host Startup Configuration Flow Chart
Figure (4) is a flow chart of how the Host may implement its startup sequence to synchronize with the Module.
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Figure 4: Host Startup Configuration Flow Chart
Startup Sync due to unexpected Host reset (Module Running State = Already Running)
The first byte of the Startup Sync Request Command(see /wiki/spaces/SPRHA17/pages/37093548for Startup Sync Request ) indicate the current running state of the module i.e., Running State indicates whether the Module has just powered up or is already running. If the Running State indicates the latter, it signifies that the Host experienced a unilateral reset. In this case, the Module will have retained all its application cache and attribute values, but will suspend network operations and return to the Startup Synchronization phase. The module will go through the following phases:
- Send out the current state (running, configured)
- Switch to Startup Sync phase
- Send out the current state (startup sync, configured)
Note: If the Running State of the Module is Already Running the Host is not required to configure endpoints, clusters and attributes and perform updates on the values of the latter. Instead, the Host should query attribute values and cached event data from the Module in order to synchronize its internal state with that of the application.