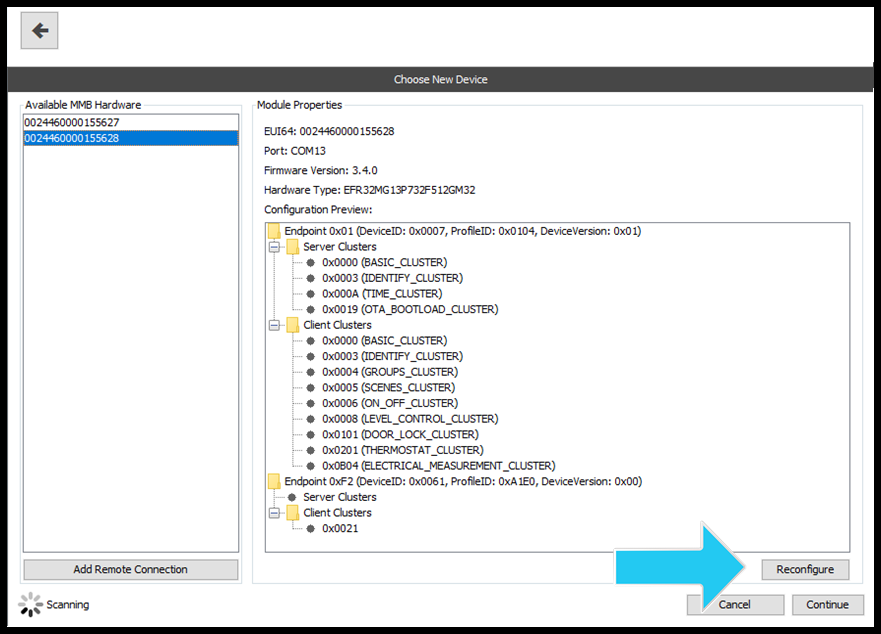
5) Execute Advanced Device Configuration (Optional)
With RapidConnect Desktop, the device configuration can be customized using the 'Advanced' configuration feature (Figure 7).
Figure 7: Advanced Device Configuration
Click on the 'Advanced >>' button ( in the figure above)
Adding an Endpoint
If required, endpoints can be added to the device configuration using the 'Add Endpoint' widget.
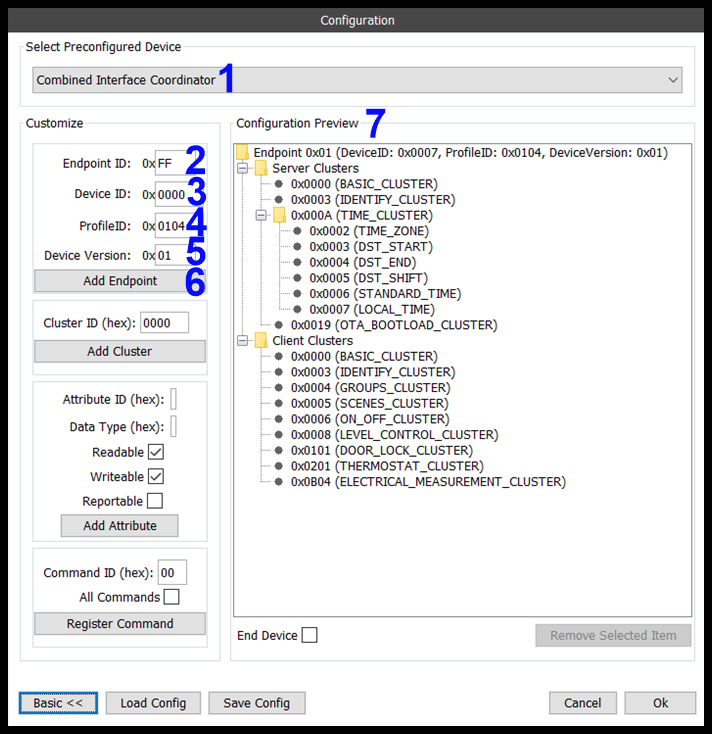
The labels in the figure above show the following:
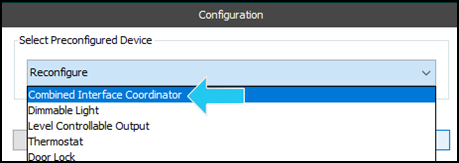
- Select Preconfigured Device: This dropdown enables you to select a device configuration to be used as a template and then modify as you see fit. In this case the "Combined Interface Coordinator" has been selected.
- New Endpoint ID: The ID(hex) of the new endpoint to be added to the device configuration.
- Device ID: The ID(hex) of the Device Descriptor represented by this endpoint, e.g. 0x0001 for Level Control Switch
- Profile ID:
- Device Version:
- Add Endpoint: Button to add the endpoint.
- Configuration Preview:
Once added, CLICK Register Command button then the endpoint will appear in the configuration preview (see below).
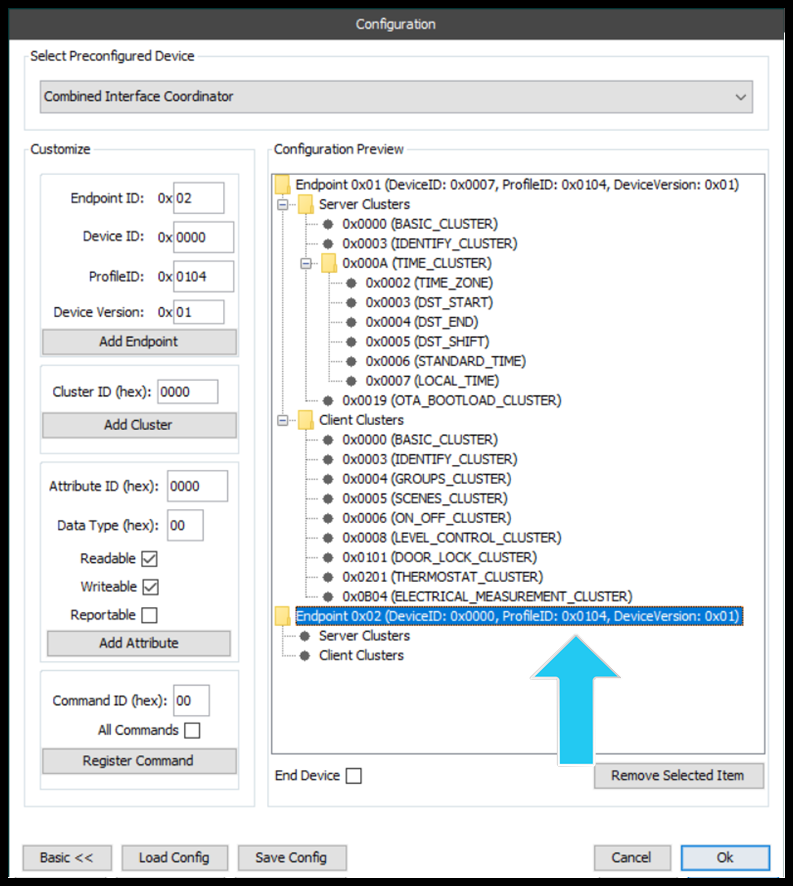
Adding a Cluster
Clusters can be added to new or existing endpoints either as a server cluster or a client cluster. Just select the desired endpoint→Server/Client Cluster group. In the example below, the newly added endpoint is selected and a client cluster is being added.
The following features are labelled in the figure above:
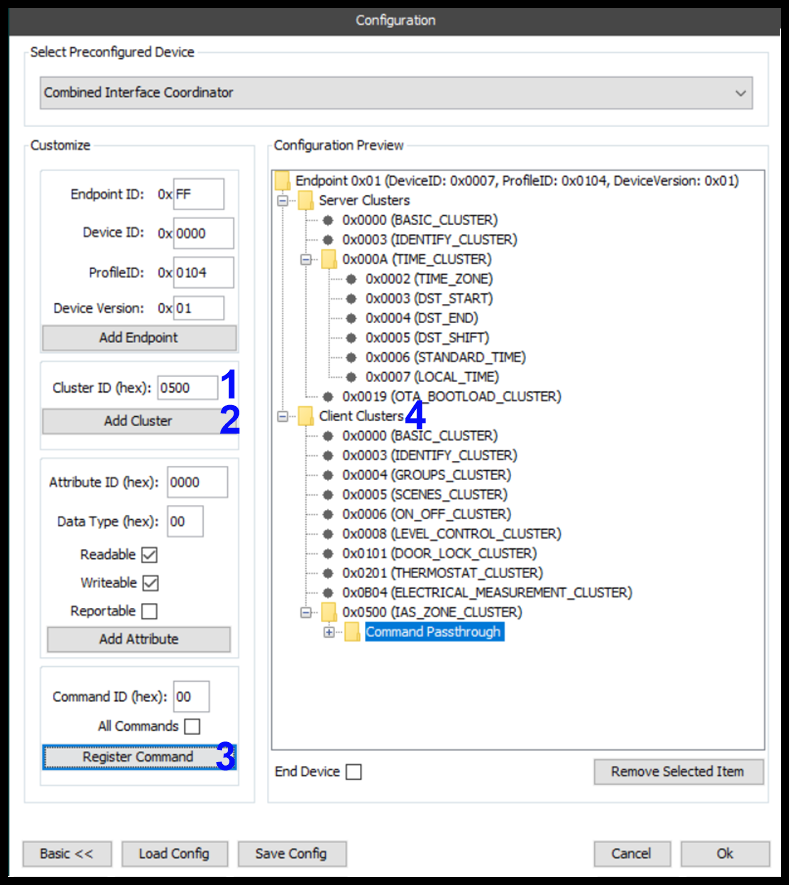
The following features are labelled in the figure above:
- Cluster ID
- Add Cluster
- Register Command
- Client Cluster
Once added, the cluster will appear in the configuration preview, under the server/client cluster root node. See the figure below.
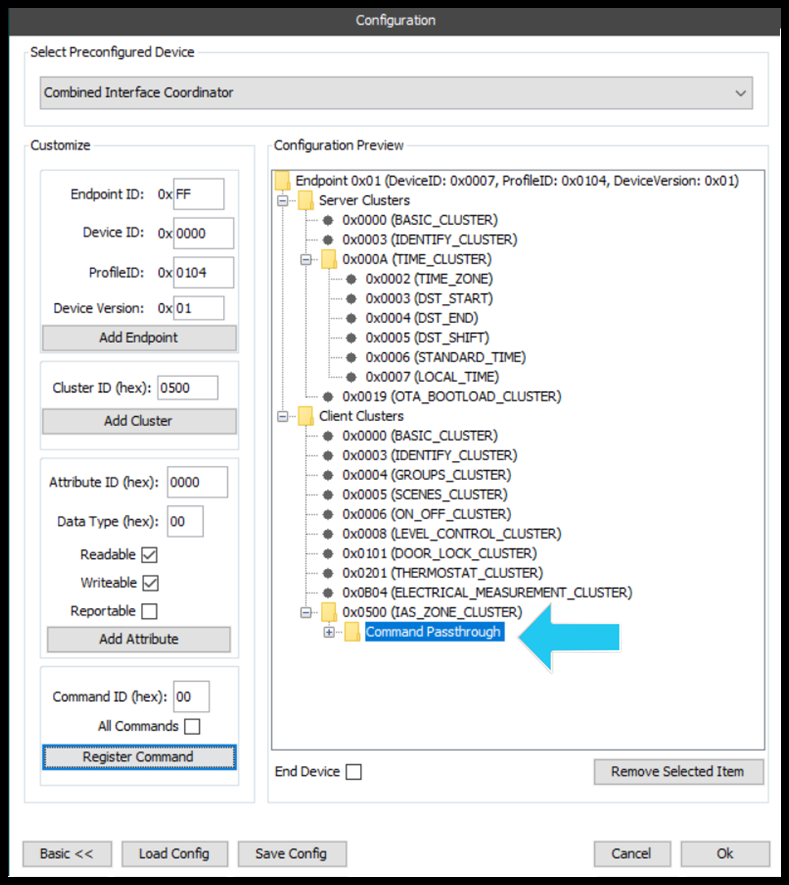
Adding an Attribute
Following the same logic above, attributes are added to clusters in the same fashion.
*Most of the commonly used and/or mandatory attributes will be part of RapidConnect's natively supported clusters and will therefore be added automatically. It should only be necessary to add Attributes to Endpoints if the Attributes are not added automatically. See here for more details.
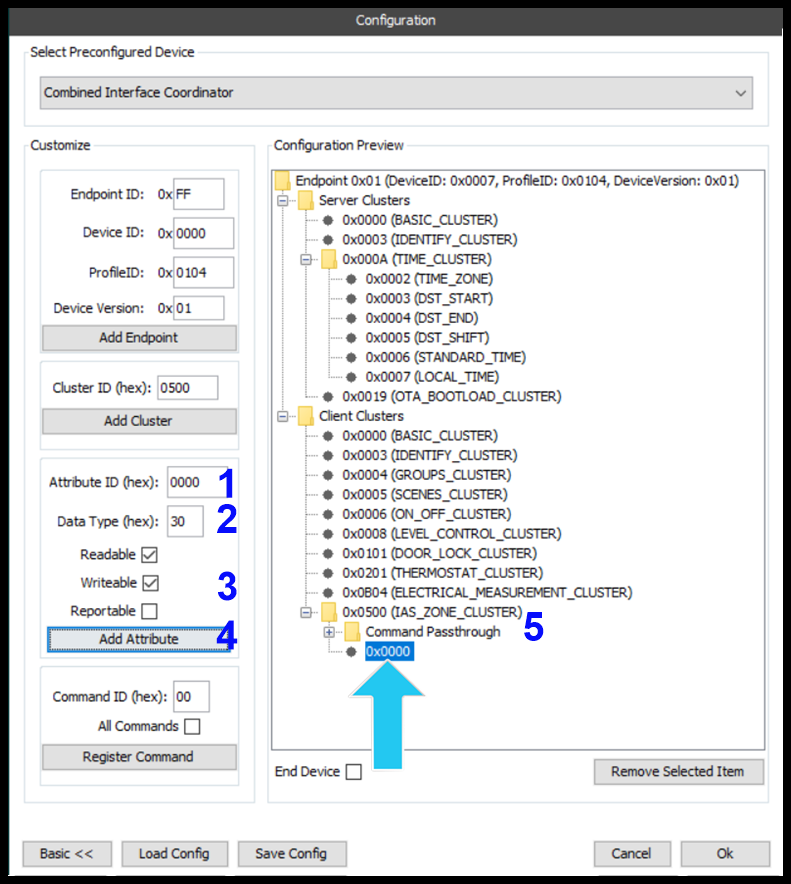
- Attribute ID: ID(hex) of the attribute to add.
- New Endpoint ID: Date Type of attribute. In this case, attribute 0x000 of the IAS Zone Cluster has a data type of 8-bit Enumeration(0x30).
- Attribute Options: Is the attribute Readable, Writable and/or Reportable.
- Add Attribute: Button to add the Attribute.
- Cluster: Cluster to add the attribute to.
Once an attribute has been added, it will be shown under the cluster, see below.
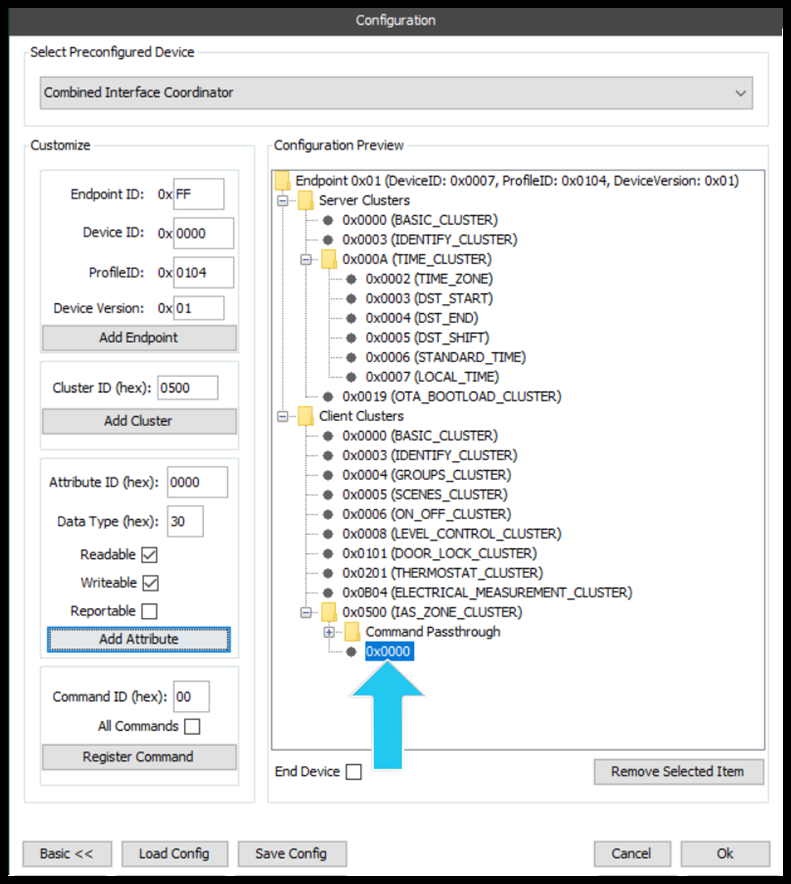
Registering a Command Passthrough
When configuring a device, it may be necessary to 'Register Commands' for passthrough. This mean that commands that are received from another device are not processed by the firmware, but instead passed up to the Host application. This may be necessary if any speciality processing of commands needs to be done, e.g. change state of other remote devices based on the command.
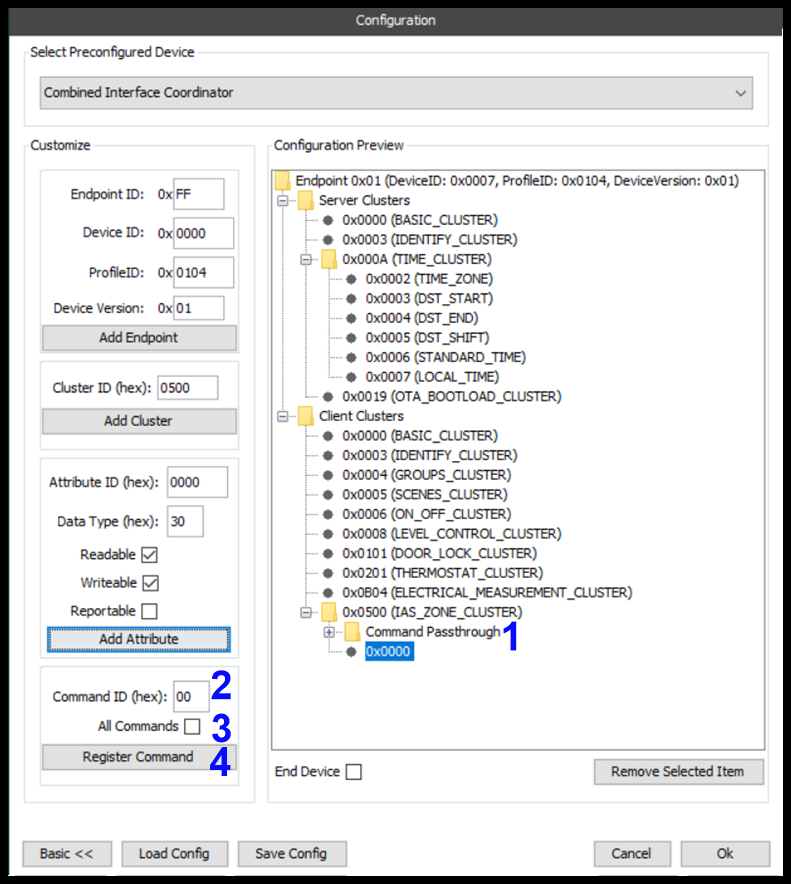
- Cluster Selection: As a specific command originates from a specific cluster, in order to passthrough the command, the cluster root node needs to be selected.
- Command ID: Each command has a cluster specific identifier. To passthrough specific commands, set the ID and register the passthrough for each command.
- All Commands: If it is desired that all commands for a given cluster are passed through, the 'All Commands' checkbox can be selected.
- Register Command: Click this button to send the Register Command Passthrough command.
Once a command passthrough has been registered it can be viewed in the configuration preview, below.